Understanding Hypoxic Red Blood Cells
What are Hypoxic RBCs?
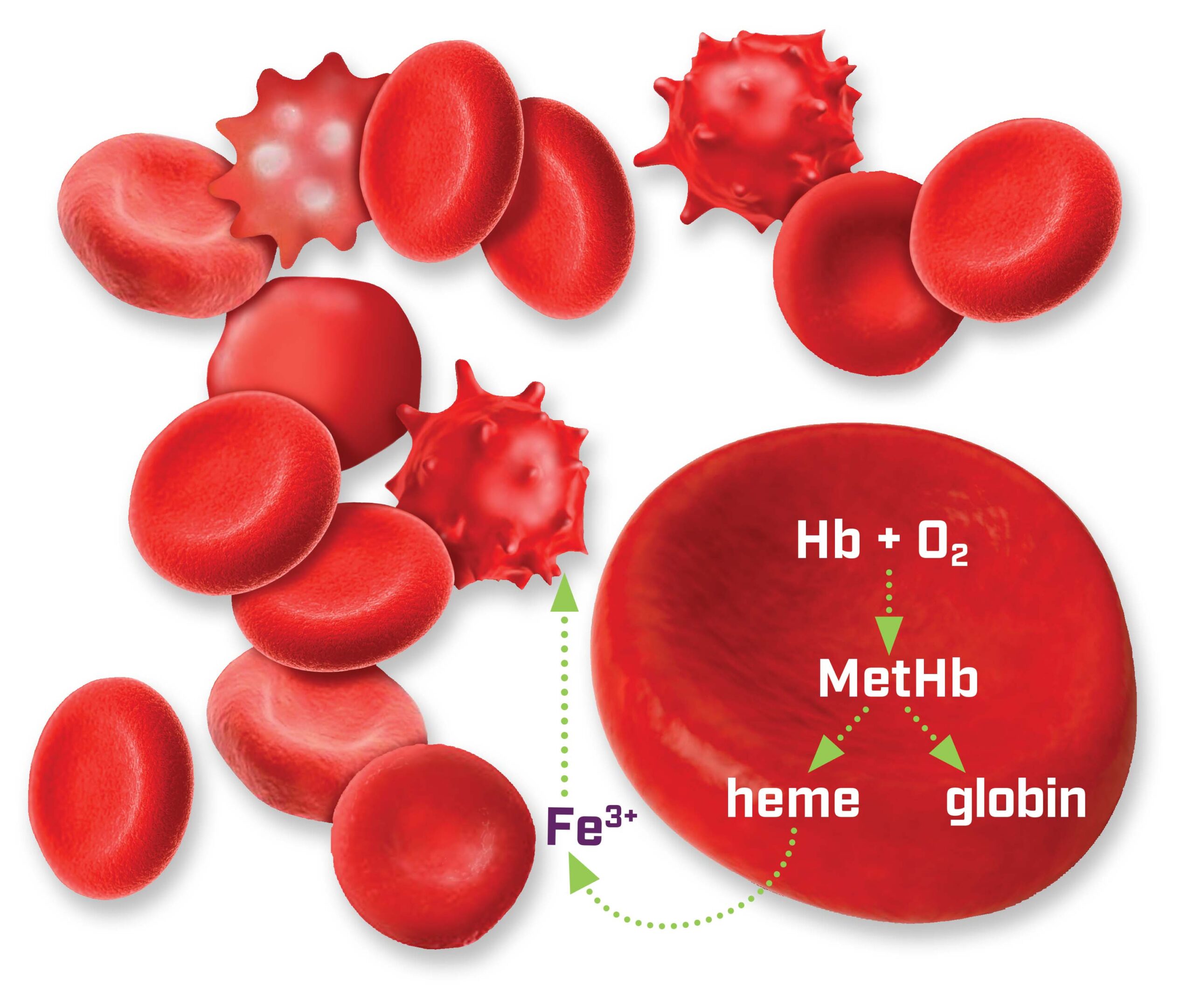
Hypoxic red blood cells (RBCs) are a specialized type of RBC created to consistently protect quality, functionality, and viability throughout their shelf life.1-5 They have been proven to mitigate the storage lesion, which is a result of detrimental effects of oxygen on RBCs during storage.1-3, 6 Hypoxic RBCs are poised to play a pivotal role in transfusions for patients who rely on them.
Hypoxic storage has been shown to reduce effects of oxidative damage1,2
How are Hypoxic Red Blood Cells Created?
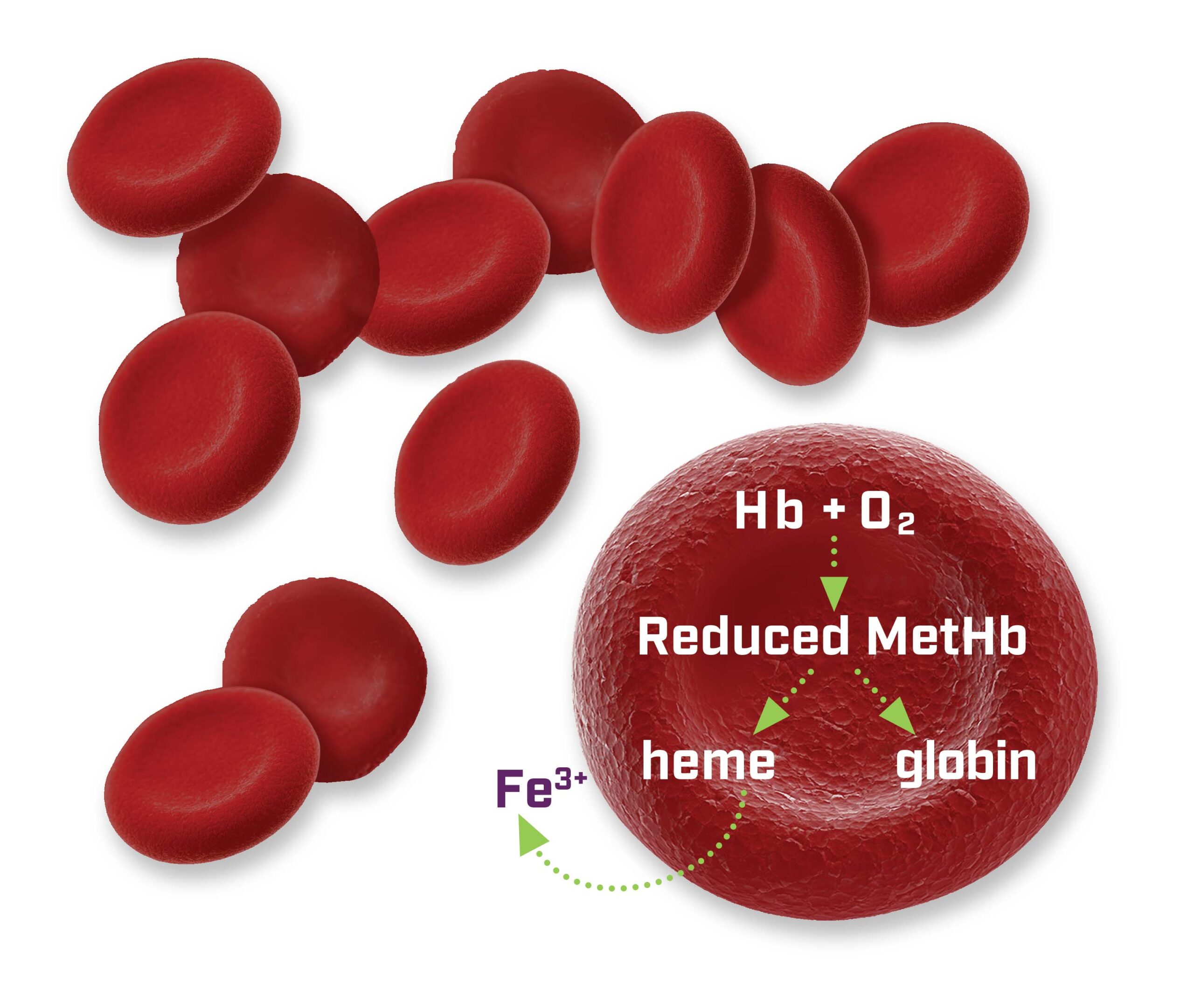
The innovative Hemanext ONE Processing and Storage System creates hypoxic RBCs by processing and storing them in a low-oxygen (hypoxic) state.
Benefits of Hypoxic Storage
- Reduces the accumulation of oxidative and metabolic damage (storage lesion)10
- Improves quality, functionality, and viability of RBCs, including deformability and endothelial adhesion 6,10,11
- Transports and offloads oxygen efficiently9
Advancing Transfusion Medicine
Hypoxic RBCs represent a meaningful advancement in transfusion medicine with great potential to improve RBC quality and enhance patient care.
Explore how Hemanext ONE is transforming transfusion medicine
1. DʼAlessandro A, Yoshida T, Nestheide S, et al. Hypoxic storage of red blood cells improves metabolism and post-transfusion recovery. Transfusion. 2020;60(4):786-798. 2. Yoshida T, Prudent M, D’Alessandro A. Red blood cell storage lesion: causes and potential clinical consequences. Blood Transfus. 2019;17(1):27-52. 3. Yoshida T and Shevkoplyas SS. Anaerobic storage of red blood cells. Blood Transfus. 2010;8(4):220-36. 4. Rabcuka J, Blonski S, Meli A, et al. Metabolic reprograming under hypoxic storage preserves faster oxygen unloading from stored red blood cells. Blood Adv. 2022; 6(18):5415-5428. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007774. 5. Dumont LJ, Yoshida T and AuBuchon JP. Anaerobic storage of red blood cells in a novel additive solution improves in vivo recovery. Transfusion. 2009;49(3):458-64. 6. Karafin MS, Field J, Ilich A, et al. Hypoxic storage of donor red cells preserves deformability after exposure to plasma from adults with sickle cell disease. Transfusion. 2022;1-10. Doi: 10.1111/trf.17163. 7. Orlov D and Karkouti K. The pathophysiology and consequences of red blood cell storage. Anesthesia. 2015;70(Suppl. 1):29-37. doi: 10.1111/anae.12891. 8. Yoshida T and Shevkoplyas SS. Anaerobic storage of red blood cells. Blood Transfus. 2010;8(4):220-236; doi: 10.2450/2010.0022-10. 9. Rabcuka J, Blonski S, Meli A, et al. Metabolic reprograming under hypoxic storage preserves faster oxygen unloading from stored red blood cells. Blood Adv. 2022; 6(18):5415-5428. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007774. 10. DʼAlessandro A, Yoshida T, Nestheide S, et al. Hypoxic storage of red blood cells improves metabolism and post-transfusion recovery. Transfusion. 2020;60(4):786-798. 11. Burns JM, Yoshida T, Dumont LJ, et al. Deterioration of red blood cell mechanical properties is reduced in anaerobic storage. Blood Transfus. 2016;14(1):80-8. doi: 10.2450/2015.0241-15.
